Development of an ultra-precision dispense solution for a Class 3 medical device implant
Automated precision dispensing is an important process step in many projects we encounter specifically in the medical device, consumer electronics and battery manufacturing industries. Achieving repeatability in dispensing is non-trivial mainly due to the characteristics of the liquids or suspensions used such as viscosity, surface tension, and setting times.
At DWFritz, we have significant expertise in precision dispensing to the point where we have developed our own proprietary solution. In order to de-risk a project, DWFritz has developed effective methods called PoP’s (Proof-of-Principle) that take some of the most challenging processes of the production line and innovate a solution in our engineering lab in order to assess, and develop the best manufacturing method that meets spec.
Medical Implant Project
In a recent production line that we developed for a Tier-1 medical device customer, DWFritz conducted several PoP’s to qualify our precision dispensing methodology. The medical device implant was approximately 5mm x 10mm (about the size of a grain of rice) and was constructed using three different silicon translucent components. The FMEA study identified high-risk areas like dispense. This challenge required determining the best tooling to dispense a continuous and controlled amount of adhesive around the part circumference.
The study assessed the dispense requirements to assemble the device across several different assembly steps. The objective of the dispense study was to identify a production level dispense solution by comparing and contrasting several different two-part epoxy dispense technologies. Our goal was to determine each technology’s ability to dispense volumes of <50nL with a high degree of volumetric accuracy and repeatability.
The effort was guided by a structured design of experiment and a dedicated prototype setup to perform the testing. And the goal at the outset was to leverage the solution into the commercial high-volume, automated manufacturing cell. We conducted a comparative analysis for both qualitative data and quantitative observations to determine operational performance across four distinct characteristics, including accuracy, uniformity, suitability, and serviceability.
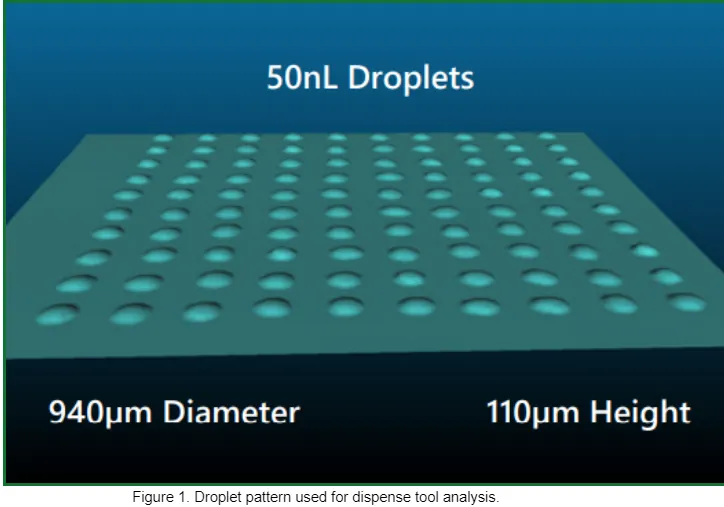
To conduct the analysis, we measured dispense shot size repeatability, minimum shot size, and dispense volume. The most challenging part of the study was creating a metrology system that could accurately measure very small transparent adhesive droplets using advanced 3D sensor technology. Figure 1 shows the droplet pattern used for analysis of the off-the-shelf dispense products.
Automated Vision Inspection in Medical Device Manufacturing
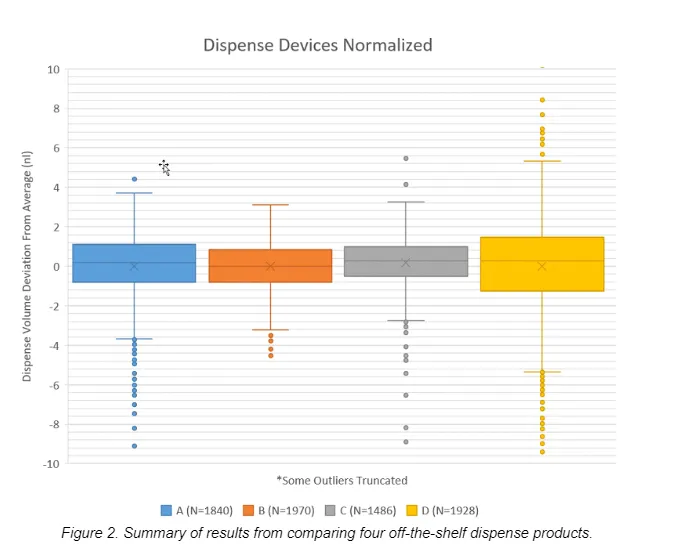
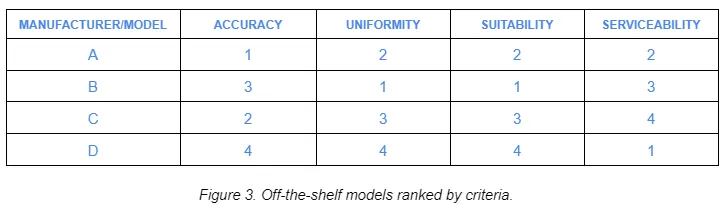
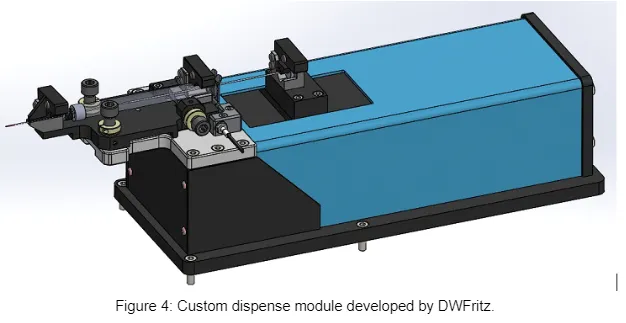
After the month’s long study, we determined that none of the off-the-shelf micro-dispense products could successfully fulfill all of the necessary requirements. In particular, we encountered issues with serviceability, accuracy, and repeatability caused by the lack of motion control and feedback. A summary of test results that show dispense volume deviations of the various off-the-shelf products are shown in Figures 2 and 3. Based on this outcome, we developed a custom dispense module (see Figure 4) that consisted of a new pump and a precision stage with high-precision linear encoder motion control feedback to achieve <1nL standard deviation for the required droplet volumes.
Contrast this with skipping the PoP step and simply selecting a dispense solution based on the published specifications, then seeing the results only after the automated system was built. This approach would have negatively affected the budget and timing due to re-design, re-build, and re-testing. Performing the proof-of-principle study also allows the separation of the system variables that can influence the adhesive testing evaluation.
Conclusion
The PoP studies helped to de-risk the project and enabled DWFritz to develop our own state-of-the-art precision dispense solution that eventually dispensed a 35nL, 80 micron wide bead in the final production system that we developed.
